Why Ethereum 2.0 will not fix gas fees
And why gas fees might keep increasing on the mainnet
As we all know, Ethereum 2.0 was supposed to come and save us from high gas fees. Too many users worldwide cannot afford to transact on Ethereum because it is just too expensive. I am here to tell you that Ethereum 2.0 will not make transaction fees go down.
I know what you are probably feeling right now…
What the @!#$&*(insert your favorite swear word) do you mean ETH 2.0 will not fix gas fees 😡!?
Have we all gotten scammed and bamboozled by Vitlaik? Is ETH a shit coin?
Should we just sell our Ether, leave the ecosystem for good and start using Cordano and Solana?
What else are you going to tell me?
Ethereum 2.0 will never come.
Ethereum 2.0 has indeed been canceled and won't be released anytime soon, disappointing those who are hoping for an update to fix high gas fees.
But it's not all bad news, as Ethereum is not becoming stagnant or abandoned. In fact, it is evolving with some changed priorities and perspectives that would only make it better.
But where did the term Ethereum 2.0 even come from?
To answer that, we need to take a quick look at Ethereum’s history.
The origin of the term Ethereum 2.0
Back in 2019, the core Ethereum developers already knew that scaling the network was necessary for any large-scale adoption, so they created a roadmap to achieve that scalability.
The team named it “The Road to Serenity,” which would become synonymous with Ethereum 2.0.
This Roadmap had three major components: Beacon Chain, Shard Chains, and eWASM.
Step 1: Beacon chain
A Proof of Stake chain would replace the Proof of Work chain that Ethereum was on(and still is). This chain would become the new consensus mechanism, where new transactions will be confirmed and added to the blockchain. The Beacon Chain would increase decentralization and improve the security of the Ethereum network.
Step 2: Shard Chains
This was supposed to be the core feature for the scalability of the network. It would split the network into 1024 shard chains and would process the data in parallel(at the same time). The Beacon Chain would monitor and validate all the shard chains. A single shard chain(out of the total of 1024) will also be monitored by 128 nodes. Every node will have a validator who is staking 32 ETH. The staking will take place on the Beacon Chain.
Step 3: eWASM
The final piece of Ethereum 2.0 was supposed to be a new Virtual Machine called Ethereum-flavored Web Assembly (eWASM).
This was supposed to be one of its features:
“With the switch to Ethereum 2.0 and the Beacon Chain, the network’s virtual machine will be upgraded to eWASM, a virtual machine based off Web Assembly, which is defined by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) as an open-source standard.”
I have no idea what this means, but it sounds pretty cool and advanced.
The other interesting feature of eWASM was supposed to support multiple coding languages besides Solidity. Writing smart contracts in pure JavaScript? Maybe…
Reality
The crazy thing is that all the updates mentioned above were supposed to be implemented by the year of 2020/2021.
As of this writing(February 2022), we are not even done with Step 1!
Currently, the Beacon Chain is still in the testing phase, and Ethereum hasn’t switched from Proof of Work(PoW) to Proof of Stake(PoS).
The good news is that the Merge(transition from PoW to PoS) might take place in the summer of 2022. At least this timeframe is an educated guess among the expert Ethereans of the ecosystem.
Important:
The core dev team of Ethereum has not confirmed this estimate, and no official date for the merge has been given.
Regardless of when the merge happens, it will not make gas fees lower. The merge or switching to PoS is NOT Ethereum 2.0. The beacon chain will improve the network's security, increase decentration, and reduce the network's energy consumption by 99%.
But again, it will not reduce gas fees.
The gas fees on the Ethereum mainnet(L1), will remain roughly the same. Fees might increase with time, and I will explain why later in this article.
Since it is already 2022 and the merge still did not occur, the core Ethereum team decided that Eth2 is not appropriate. The original timeline for the Ethereum roadmap had to be modified to catch up to reality.
Instead of using Eth1 and Eth2 to talk about the merge, the terms execution and consensus layers are more useful.

- Source: The Ethereum Foundation
Ethereum.org has a great article on this.
If you currently use the Ethereum mainnet(L1) for transactions, the EVM(Ethereum Virtual Machine) is responsible for both the execution and the consensus.
The Execution Layer is a part of the virtual machine that executes the programs written in Solidity. These programs can vary in complexity, and they tend to be very resource-intensive.
EVM is a giant decentralized computer, and due to being decentralized, it is very slow. If there are a myriad of highly resource-intensive programs running on the EVM simultaneously, the network can slow down, and gas will be high.
The good news is that the execution portion can be moved to a place where the computation can be executed in a more efficient manner. This place has a name, and it is what we refer to as Layer 2 chains or L2s for short. L2s tend to be more centralized, which helps with computation and execution efficiency.
While decentralization is not necessary for computation and execution, it is essential for consensus. This ingredient is vital for the network’s long-term security. If the network wants to be safe from government attacks and remain permissionless long-term, the consensus layer must remain decentralized.
The responsibility of the consensus layer is straightforward. It has to fill up blocks with data and add them to the blockchain. The consensus layer is also responsible for ensuring that all the data is non-fraudulent. Besides those functionalities, the rest can be moved to L2s.
Ethereum 2.0 is already here
Well, kind of. The roadmap from 2019 is nowhere near completion. But the scaling solution that will reduce gas fees is already here, and it is already increasing Ethereum's throughput. Rollups are that solution.
The great news is that anyone can use rollups right now!
Want to swap a token but get priced out by Ethereum(L1) gas fees? How does a 97% lower fee sound? That is possible with rollups like zkSync, Arbitrum, and many others.
Are you concerned about security? No problem! The L2 rollups are as secure as Ethereum because all transactions are confirmed on mainnet Ethereum.
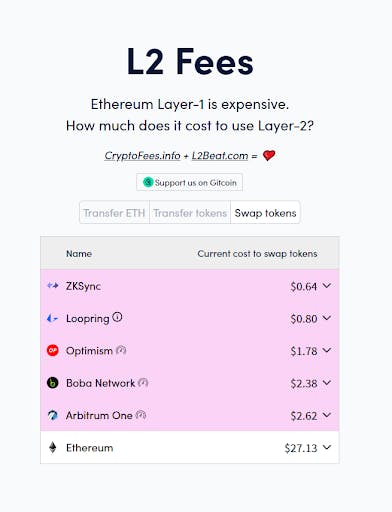
- A breakdown of fees for L2s vs. Ethereum mainnet
How can these fees be up to 97% lower, yet remain as secure as Ethereum?
Simple.
The rollups are only responsible for the execution portion, and they don’t have the hardware limitations that the EVM(Ethereum Virtual Machine) has. Actually, rollups can also be considered their own EVMs that run independently.
Another way to understand rollups is to use the .zip file analogy. The process of compressing a .zip file is computationally intensive, the same as executing complex transactions on the mainnet. This demanding part can be moved to a rollup, and all the heavy lifting can be performed there. Once the compression part is completed, the .zip file(a rollup) can be transferred to L1 to be confirmed, bypassing all the fees that will be incurred if computation was performed on the L1.
Currently, there are two types of rollups; optimistic and zk(zero-knowledge) rollups.
Optimistic rollups rely on the assumption that most people are good actors. In the case of bad actors on optimistic rollups, individuals monitor the transaction to make sure they are correct.
Zk rollups rely primarily on cryptography and advanced mathematics to ensure that the transactions are valid.
It is worth the time to explore, use, and build on these rollups, to understand how rollups work. Most of them don’t have a token yet, so early users will most likely be rewarded with an airdrop in the future 😉.
Eventually, we could see most users migrate to L2s because the majority of transactions will be occurring there.
We could see dapps do things not currently possible on Ethereum L1 due to current expensive transactions.
Also, with faster and cheaper transactions, there will be an increase in experimentation and innovation.
Maybe we will see decentralized Twitter or complex multiplayer games with modern graphics and run on cutting-edge gaming engines. The future is exciting.
Why will fees keep increasing on the mainnet?
As the number of users keeps increasing on Web3, so will the number of rollup transactions. Even though L2s performed the computation, the transactions still need to be added and confirmed on Ethereum L1. As this trend continues to increase on Ethereum L1, fees will keep growing. Eventually, it will become so expensive that not even the whales will be able to afford to use the mainnet Ethereum for day-to-day transactions, only the rollups will. The rollups are happy to pay those fees because they get the security of Ethereum. Also, L1 fees will be a small fraction compared to the fees rollups will generate from users.
TL;DR
- The term Eth2 or Ethereum 2.0 is being phased out
- It is being replaced by consensus layer and execution layer
- Switching to a Proof of Stake Beacon chain or the Merge is commonly(and incorrectly) referred to as Ethereum 2.0
- Switching to the proof of stake Beacon chain will not lower gas fees!
Using Layer 2 chains(L2s) is currently up to 97% cheaper than mainnet Ethereum
(All of L2s are secured by Ethereum)
(These chains are Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync, StarkNet, and many more)
Most activity will be taking place at these L2s in the future
(Currently, these L2s don’t have a token, but there is a high possibility of an airdrop in the future if you use them now)
Conclusion
Personally, I am very bullish on the Ethereum ecosystem and I look forward to it’s future with excitement. With L2s becoming more popular we should see new users joining, who were previously priced out by mainnet gas fees.
Ethereum will of course still continue to scale. If you are curious about how exactly that will happen, take a listen to this podcast. It will inform you how the next six years will shape this blockchain.
To dive deeper into how Ethereum will scale, here is a great post from polynya.eth
